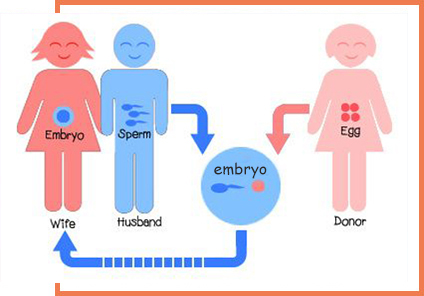
Third party reproduction refers to the use of donor egg or donor sperm or surrogate to enable the couple to become parents.
- Egg donation
When the female partner is unable to produce healthy egg then they are taken from a healthy young woman (the egg donor) which are then fertilised with the sperms of the male partner (husband) so as to form a fertilized egg resulting into embryos which are then transferred into the female partner’s uterus.
What is the process of Egg Donation
The first step is a selection of an anonymous donor who is approved after thorough medical and genetic screenings. Egg donors are recruited through ART banks. After selection, the donor’s ovaries are stimulated by a stimulation regimen to produce multiple eggs which are then retrieved and fertilized by IVF/ICSI using the male partner’s sperms. The embryos formed are transferred into the uterus of the female partner.
Who is offered egg donation?
- Advanced maternal age with poor ovarian reserve
- Multiple failed IVF/ICSI attempts with self eggs
- Female with known genetic diseases that can affect the fetus
- Sperm donation
Donor sperm may be required in cases of:
- Azoospermia (absence of sperms) where sperms could not be retrieved medically or surgically.
- Risk of transmission of genetic disease to the offspring
Donor semen samples are provided by ART banks. The sperm donors undergo a series of investigations before their semen sample is collected. Then semen sample is frozen for quarantine period of 6 months. According to the physical characteristics (height, skin color, hair color, eye color) and the blood group of infertile couple, a request to ART bank is sent and the semen sample is procured. The sample is warmed and checked for sperm count and motility before using it for ART procedures. Consent of both partners is taken prior to use of donor sperm. Donor sperm can be used for both Intra-uterine Insemination (IUI) and In-Vitro fertilsation (IVF).
- SURROGACY:
Surrogacy is an arrangement where a woman (surrogate mother) carries the baby of intending parents through IVF in her uterus. She hands over the baby to intending parents at delivery. The gametes belong to the genetic parents or sometimes donor but not to the surrogate mother. This treatment procedure is supported with a legal document.
Medical conditions necessitating gestational surrogacy are:
- Woman with absent uterus or abnormal uterus or if the uterus is surgically removed due to any medical conditions such as gynecological cancers.
- Repeated IVF failures
- Any illness that makes it impossible for woman to carry a pregnancy to viability or pregnancy that is life threatening.
- Fertility preservation:
Fertility preservation is a broad term which involves many procedures to retain fertility in men and women. This mainly applies to people who are being treated for cancer or other illnesses which might prevent them from having children. It may also apply to those who wish to postpone child bearing due to personal or social reasons. It includes:
Freezing of sperms
A person who might undergo treatment which might potentially make him infertile – can produce semen by masturbation and get it frozen for future use. It is best to freeze multiple samples (if time permits).
Freezing of eggs
It involves administration of medications for a period of two weeks or more to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, which are then collected by a minor surgical procedure under general anaesthesia. These eggs are then frozen for future use.
Freezing of embryos
For married women, the eggs collected can be fertilised with the husband’s sperm (IVF or ICSI) and then cultured to form embryos. These embryos are then frozen. When the woman is ready to initiate pregnancy, the embryos are thawed and transferred into the uterus for further growth and development of pregnancy.
Ovarian transposition (oophoropexy)
This surgical procedure is sometimes recommended if radiation is being planned to your pelvis. The ovaries are surgically repositioned just before radiation therapy so that they are as far away as possible from the planned radiation field. This though does not always completely protect the ovaries. After completion of the radiation, you might need to have the ovaries repositioned again or use IVF to conceive.